- Making web requests With Python's requests (pip install requests) library we're getting a web page by using get on the URL. The response r contains many things, but using r.content will give us the HTML. Once we have the HTML we can then parse it for the data we're interested in analyzing.
- Mar 18, 2021 Web scraping with Python is easy due to the many useful libraries available A barebones installation isn’t enough for web scraping. One of the Python advantages is a large selection of libraries for web scraping. For this Python web scraping tutorial, we’ll be using three important libraries – BeautifulSoup v4, Pandas, and Selenium.
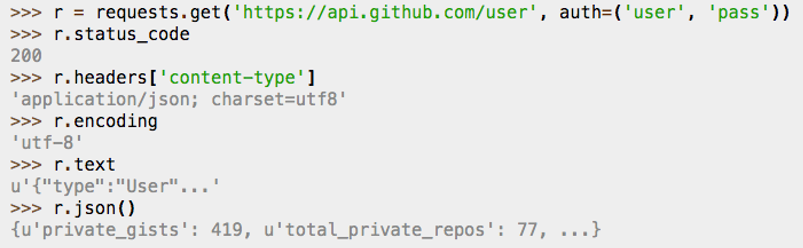
- Loading Web Pages with 'request' The requests module allows you to send HTTP.
- We have learned how the urllib and request two python modules can help in web scraping from scratch, there are many ways to execute your web scraper like in the previous article we used selenium for web scraping then we combined selenium with beautiful soup and now we have integrated request module instead of selenium with beautiful soup.
I’ve recently had to perform some web scraping from a site that required login.It wasn’t very straight forward as I expected so I’ve decided to write a tutorial for it.
For this tutorial we will scrape a list of projects from our bitbucket account.
Sessions in scraping services are used mostly to send a put request that is to fill a form like Login form etc. They are also used to send multiple requests and scrape data in parallel. Now let’s see how to use cookies and session with python requests library.
The code from this tutorial can be found on my Github.
We will perform the following steps:
- Extract the details that we need for the login
- Perform login to the site
- Scrape the required data
For this tutorial, I’ve used the following packages (can be found in the requirements.txt):
Open the login page
Go to the following page “bitbucket.org/account/signin” .You will see the following page (perform logout in case you’re already logged in)
Check the details that we need to extract in order to login
In this section we will build a dictionary that will hold our details for performing login:
Web Scraping With Python Beautifulsoup Requests & Selenium
- Right click on the “Username or email” field and select “inspect element”. We will use the value of the “name” attribue for this input which is “username”. “username” will be the key and our user name / email will be the value (on other sites this might be “email”, “user_name”, “login”, etc.).
- Right click on the “Password” field and select “inspect element”. In the script we will need to use the value of the “name” attribue for this input which is “password”. “password” will be the key in the dictionary and our password will be the value (on other sites this might be “user_password”, “login_password”, “pwd”, etc.).
- In the page source, search for a hidden input tag called “csrfmiddlewaretoken”. “csrfmiddlewaretoken” will be the key and value will be the hidden input value (on other sites this might be a hidden input with the name “csrf_token”, “authentication_token”, etc.). For example “Vy00PE3Ra6aISwKBrPn72SFml00IcUV8”.
We will end up with a dict that will look like this:
Keep in mind that this is the specific case for this site. While this login form is simple, other sites might require us to check the request log of the browser and find the relevant keys and values that we should use for the login step.
For this script we will only need to import the following:
First, we would like to create our session object. This object will allow us to persist the login session across all our requests.
Second, we would like to extract the csrf token from the web page, this token is used during login.For this example we are using lxml and xpath, we could have used regular expression or any other method that will extract this data.
** More about xpath and lxml can be found here.
Python Best Web Scraper
Next, we would like to perform the login phase.In this phase, we send a POST request to the login url. We use the payload that we created in the previous step as the data.We also use a header for the request and add a referer key to it for the same url.
Now, that we were able to successfully login, we will perform the actual scraping from bitbucket dashboard page
In order to test this, let’s scrape the list of projects from the bitbucket dashboard page.Again, we will use xpath to find the target elements and print out the results. If everything went OK, the output should be the list of buckets / project that are in your bitbucket account.
Web Scraping Requests Python Tutorial

You can also validate the requests results by checking the returned status code from each request.It won’t always let you know that the login phase was successful but it can be used as an indicator.
for example:
Web Scraping Requests Python Code
That’s it.
Web Scraping Requests Python Programming
Full code sample can be found on Github.
